
Under a series of economic stimulus measures, China's major economic indicators in August have risen in August, but it has not dispelled the market's concerns about the weakening of the world's second largest economy.Is the recovery of China's economy sustainable?How long will the property market still fall?Will the Chinese economy go to "Japan"?
Chinese diplomats, economic authorities, and official media have taken turns this month to refute the "Chinese economic collapse theory".
The background of this round of public opinion warfare is that the economic data of China is weaker than expected in the first half of the year, and many Western media have successively made pessimistic predictions on China's economic prospects.
U.S. President Bynden compared the Chinese economy in early August to a "ticking timing bomb"; Australian Finance Minister Chammer said in the end of the month that the "worrying" Chinese economy may be in Australia.Bring stress.
After the Chinese embassy spokesman Liu Pengyu and the Ministry of Foreign Affairs spokesman Mao Ning successively refuted the theory of declining the Chinese economy, Chinese official media have published three series of comments in the past week, saying that the "Chinese economic collapse theory" is destined to collapse again.Cong Liang, deputy director of the National Development and Reform Commission of China, also emphasized at the routine blowing meeting of Wednesday (September 20) that the theory of singing in China "has never been realized in the past, and it is destined to be realized in the future."
Cong Liang admits that there are indeed many difficulties in China's economic operation. Especially after three years of epidemic, economic recovery must be a wave -type development and twists and turns.
He also pointed out that with the appearance of the official stimulus policy, the economic operations continued to recover in August, most indicators improved marginal improvement, positive factors accumulated increased, and social expectations improved.
China officially introduced an intensive economic stimulus policy in the second half of the year, from the reduction of interest rate cuts to relaxation restrictions, covering many fields such as finance, consumption, real estate and private investment.In August, the economic indicators rose in an all -round way, the growth rate of industrial added value and retail consumption exceeded expectations, and the decline in exports narrowed.

Xing Ziqiang, the chief economist of Morgan Stanley China, has been interpreted from August data. China ’s travel consumption has maintained a strong recovery momentum, and the industrial sector has also ended for a half -year destocking cycle.He is optimistic that the Chinese economy "began to come out slowly from the bottom of the valley."
Chen Guangyan, a professor of economics at Nanyang University of Science and Technology in Singapore, predicted during an interview with Lianhe Zaobao. With the recent policy support, the growth rate of China's GDP (GDP) in the third quarter of China may bottom out to 4.8 %, and the fourth quarter will return slightly in the fourth quarter.To 5.3 %, the economic growth throughout the year can reach 5.2 %, the official growth target of about 5 %.But he also warned that the downturn of real estate is the biggest uncertain factor in future growth.
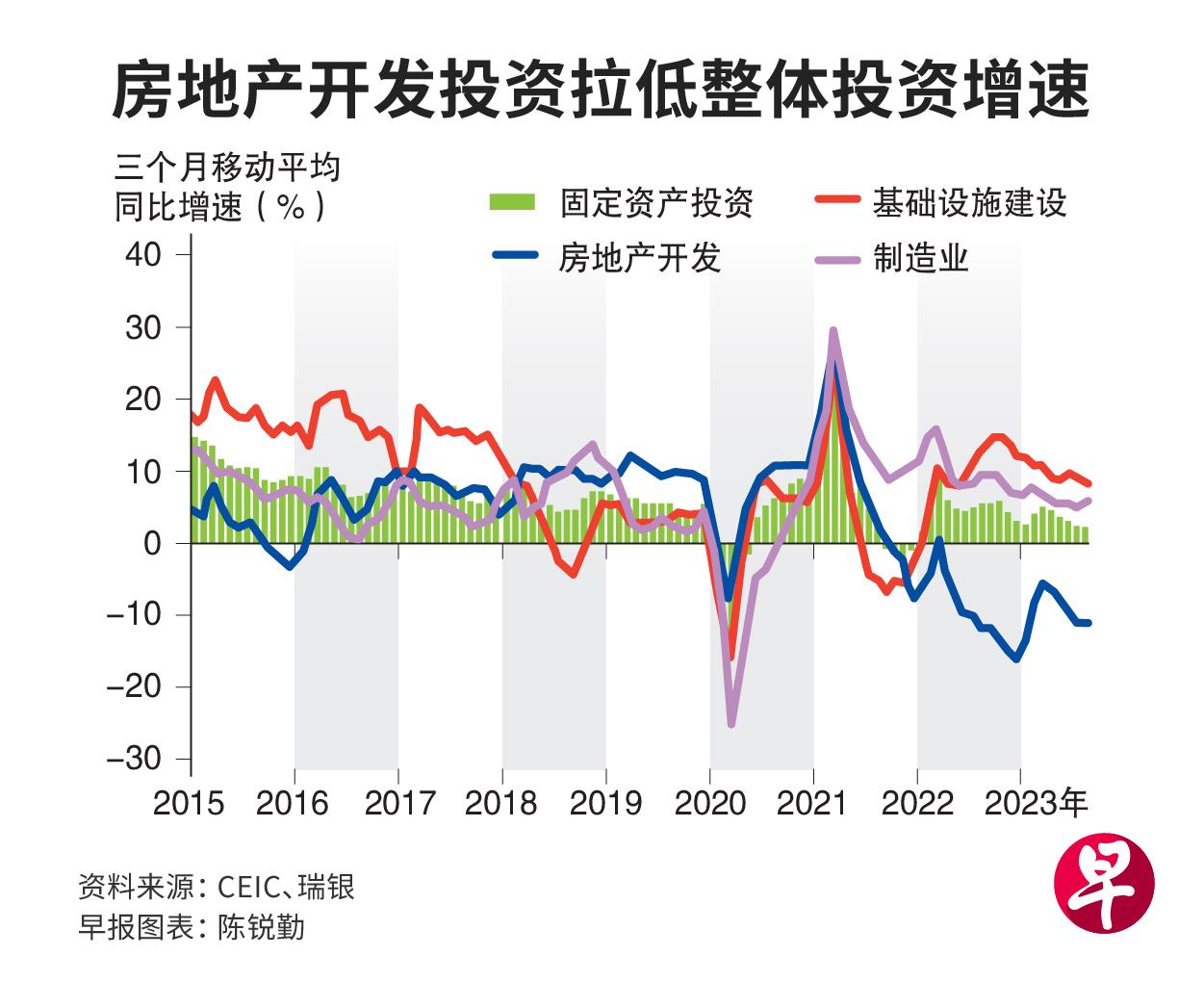
In the first eight months of this year, investment in fixed assets increased by 3.2 % year -on -year, and the increase continued to decline.As both infrastructure and manufacturing investment rose, this year, a total of 8.8 % of real estate development investment has become the main reason for lowering the overall investment.Although the official has continued to increase the property market since August, Chen Guangyan believes that it is difficult for real estate to stop falling and rebounding this year.
In addition to the deteriorating property market, the continuous high unemployment rate, high -built local debt stations, and continuous tension Sino -US relations are all major risks that China's economy has not yet resolved.Lu Ting, the chief economist of Nomura China, believes that the growth of consumption growth after the peak of the summer travel will fall, and the decline in export and real estate investment will cause industrial added value to still face resistance. At present, it is too early to assert that the economy bottoms.
Xing Ziqiang also pointed out at the Chinese Macroeconomic Forum a week ago that the property market is still in the process of deleveraging, and the impact on the economic may still deepen, which not only dragged down investment, but also spread to residents' consumption.In this process, if you face the negative feedback cycle of debt and price downward, the more you want to deleveraging, the higher the leverage.
Looking back on the response of the Great Depression in the United States and the breakdown of the Japanese bubble, Xing Ziqiang believes that China should launch a package of macro -easing policies in a timely and effectively, especially the coordination and looseness of fiscal and monetary policy to adjust the economic structure and prevent financial risks.Break the negative feedback cycle.
The former president of the People's Republic of China Yi Gang also wrote an article on the CPPCC on September 20 that the Chinese economic recovery has slowed down since the second quarter, and its economic endogenous power and market confidence have been weak.Policy regulation, effectively support the expansion of domestic demand, and promote a virtuous circle of economic.
Compared with the US government's debt ratio close to 100%, China's central financial and health is in good health. The debt ratio accounts for only 20%of GDP, and there is still a lot of policy space.However, in addition to slightly cutting interest rates and reduction, the government has not introduced large -scale stimulus measures for market expectations.Policies are expected to fall again and again, causing the Chinese stock market and RMB exchange rate to fall into a downturn.
Xie Dongming, director of the Research Department of the Greater China District of Overseas Chinese Bank, said in an interview that due to insufficient confidence, the forward -looking function of China's financial market has been greatly weakened.Only when the situation really improves, this is to a certain extent dragging the overall economic recovery process to a certain extent. "
Bai Shizhen, a visiting professor at the National University of Singapore and the dean of Li Bai Financial College, believes that in the face of the current short -term pain, China's decision -making level has performed "quite well" so far."The signal they issued is to quickly raise GDP through 'big water drilling', but to pursue long -term high -quality development."
Bai Shizhen said in an interview that, even if the impact of the epidemic in the past three years, the aging population, and the intensification of geopolitical risks in the past three years, have forced the Chinese economy to shift from heavy labor to heavy innovation and gradually reduce dependence on the real estate industry."The reality is that the era of high -speed growth in China's economy has passed. In the process of transformation of high -quality development, the growth rate of 4 % to 5 % is acceptable."
When will the property market rebound?
As the economic indicators in August bottomed out, the real estate data that was still declining seemed particularly abrupt, and it was even more sweating for the property market.
The latest data released by the National Bureau of Statistics of China on September 15 shows that real estate investment has increased in August, and the prices of new commercial housing in 70 large and medium -sized cities across the country fell for three consecutive months.%, The largest decline since 2014.
Seeing this industry, which accounts for about 17 % of the GDP, has changed sharply after the short "Xiaoyangchun" at the beginning of the year. Chinese officials have launched a market rescue policy in the second half of the year.The interest rate of stock loans in stock, as well as "do not recognize loans" in four first -tier cities.Guangzhou also announced on September 20th that the purchase restrictions on some parts of the city, further releaseLoose signal.
But the market is worried that if the above measures still cannot revive housing sales, it will continue to worsen the liquidity crisis of real estate developers.Following Evergrande's mines, housing companies with a state -owned background have announced the suspension of all overseas debts. Although Country Garden has voted after multiple rounds of debtors and won the exhibition for nine domestic bonds, it has not fundamentally alleviated the pressure of debt defaults.
International rating agency Moody's September 14 will reduce its outlook on the Chinese real estate industry from "stable" to "negative". It is expected that housing sales will drop by about 5 % in the next six to 12 months.Moody's analysts believe that although the Chinese government has recently strengthened its support for the property market, the impact is "short -term"; the weak economic growth is impacting the expenditure of buyers, and the credit pressure of Country Garden has made them more cautious about risks.
Xu Gao, the chief economist of BOC International Securities, believes that the policy of "recognizing houses and not recognizing loans" has not touched the main contradiction in the current real estate industry, that is, the condition of housing companies' funds and high credit risks, so it is difficult to make the industry jump out of out of the industryMalignant cycle.
Xu Gao wrote this month that after the "three red lines" policy restricting housing enterprises' financing was launched two years ago, the bank was worried that the risk of bad debt risk was unwilling to borrow a loan for housing companies.The chain is more tight and the credit risk is higher.If this cycle cannot be broken, it will be difficult to boost the property market by relaxing the demand policy alone, but it will increase the pressure on housing prices.In the half -month launch of "recognition of houses and not recognizing loans", the real estate sales area of 30 large cities in China has not improved significantly, but second -hand housing prices in large cities such as Beijing have begun to rise significantly, which is a signal.
Yan Yuejin, the research director of the E -House Research Institute, was optimistic that as the enthusiasm for buying houses in various places increased, the sales side data will usher in a strong rebound in September and October.However, he also pointed out that the policy effect will not be transmitted to the supply side so quickly, and real estate development investment data will continue to fall this year, and it will not stabilize until next year.
He further analyzed that the most important judgment on the current real estate industry is "major changes in supply and demand relationship", especially in the context of almost a house in large cities, investing in speculation demand exit, and believes that housing prices have reached a high pointIt is expected to be strong.In addition, buyers' concerns about income stability also affect purchase decisions."Wait until the macro economy has changed, everyone has spare money, and it takes a process."
Zhang Xiaoduan, deputy dean of the Dede Liangxing Research Institute, judged that under the trend of population growth and slowing urban population growth, the overall rebound of house prices and the rapid upward rise have changed.With policy adjustments, stimulating rigidity and improving demand release will be the main goal of this round of regulation. It is expected that subsequent places will also focus on this goal.
Will the Chinese economy be Japanese?
"Will China be the next Japan?"
In the past few months, this problem has not only seen the news from China and foreign countries, but also a topic of discussion.Since the second quarter of this year, China's economic data and property markets have weakened, and the increase in household loans in advance, and the overlapping population aging has intensified the intermediate and long -term trends, which have caused many economists to see the shadow of Japan 30 years ago.

In the late 1980s, both Japanese stock markets and real estate bubbles both ruptured, and a large number of companies and families were therefore high.In order to get rid of liabilities as soon as possible, companies and individuals use cash to repay debts to repair the balance sheet, rather than investing and consumption, which has caused the Japanese economy to be stagnant for more than 10 years.
The above phenomenon is summarized as Gu Chaooming, the chief economist of Nomura Comprehensive Research Institute of "Assets Liabilities", and is one of the earliest scholars to warn the "Japanese economy".In his speech at the Soochow Securities (Hong Kong) strategy in June this year, he pointed out that China may also go through the crushing real estate bubble and move towards the decline of the balance sheet.
Although the Chinese government can avoid economic recession through large -scale fiscal stimuli, Gu Chaoming believes that in addition to solving internal problems such as the downlink of the property market and the atrophy of population, China also has to face external risks such as China -US decoupling, as well as crown disease and epidemic conditions.The impact caused by sudden factors is now "more challenges facing Japan 30 years ago."
The New York Times columnist and economist Paul Cruggman judged in the July column that China and Japan 30 years ago have too low consumption demand, reduced labor population, economic excessive relying on real estate, etc.question.However, he questioned whether China, when the economic slowdown and the high unemployment rate, China, who is "under the unstable authoritarian regime", is China who has the ability to manage a lower economic growth rate like Japan that year without causing large -scale social turmoil.
However, the two analysts and scholars visited by Lianhe Zaobao believe that there are essential differences between China and Japan that year, and China will not repeat the mistakes of Japan.
Xie Dongming, director of the Greater China Research Director of the Overseas Chinese Bank, pointed out that the number of Chinese families that have been repaying in advance this year have increased, mainly because the interest rate of stock loans is higher than the deposit interest rate. Early repayment is a rational choice to maximize the return.In addition, the credit and investment of the corporate sector are also on the rise, which is very different from Japan's stagnation during the economic recession.
From the perspective of medium- and long -term trends, Xie Dongming believes that China and Japan 30 years ago have at least three differences.First, the important reason for the Japanese asset bubble that year was a significant appreciation of the yen, and the RMB has still faced the pressure of depreciation, and the government has major control over the exchange rate.Second, the proportion of China's per capita GDP and middle -class groups is much lower than that of Japan. The breakdown of asset bubbles will not have a general impact.
"Third, China's big government and large market have a significant impact on the allocation of resources. In additionA lot of. "
Chen Guangyan, a professor of economics at Nanyang University of Technology in Singapore, pointed out that in 1990, the value of Japanese land reached 560 % of GDP, and the stock market value was equivalent to 142 % of GDP in 1989.At present, China's real estate value is about 260 % of GDP, the stock market value accounts for 67 % of the overall economy, and asset bubbles are much smaller than Japan.In addition, the Japanese urbanization rate has reached 78 % in 1990. It was only 65 % last year in China, and there is great potential to increase productivity and economic growth.
"The most important thing is that only mature industries such as cars, consumer electronics, steel and other mature industries after the burst of bubbles, and completely missed the Internet revolution that emerged in the 1990s.Many emerging industries such as artificial intelligence account for dominant positions, which will be the main growth points and pillar industries in China in the next 20 years. "
Chen Guangyan added that although the labor force caused by the aging of the population is a major challenge, China can alleviate this problem by roboticization."Some estimates show that China can increase the GDP growth rate of 0.5 to 1 percentage point through robotization."



